Simple, efficient, open-source package for Simultaneous Localization and Mapping in Python and C++ This repository contains everything you need to start working with Lidar -based SLAM in Python or C++. There is also support for Matlab and Java, though I am no longer maintaining that code.) BreezySLAM works with Python 2 and 3 on Linux and Mac OS X, and with C++ on Linux and Windows. By using Python C extensions, we were able to get the Python version to run as fast as C++. For maximum effiency on 32-bit platforms, we use Streaming SIMD extensions (Intel) and NEON (ARMv7) in the compute-intensive part of the code.
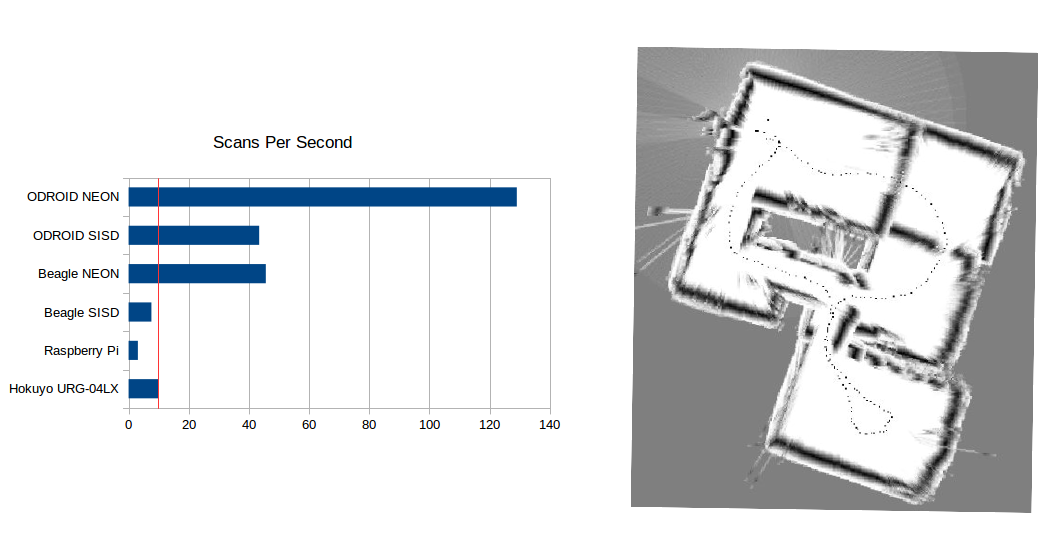
BreezySLAM was inspired by the Breezy approach to Graphical User Interfaces developed by my colleague Ken Lambert: an object-oriented Application Programming Interface that is simple enough for beginners to use, but that is efficient enough to scale-up to real world problems; for example, the mapping of an entire floor of a house, shown in the image above-right, made by a BreezySLAM user. As shown in the following code fragment, the basic API is extremely simple: a constructor that accepts Lidar parameters and the size of the map (pixels) and mapping area (meters); a method for updating with the current scan; a method that returns the current robot position; and a method for retrieving the current map as a byte array.
from breezyslam.algorithms import RMHC_SLAM
lidar = MyLidarModel()
mapbytes = bytearray(800*800)
slam = RMHC_SLAM(lidar, 800, 35)
while True:
scan = readLidar()
slam.update(scan)
x, y, theta = slam.getpos(scan)
slam.getmap(mapbytes)
If odometry is available, it can also be passed into the update method.
The BreezySLAM installation uses the popular distutils approach to installing Python packages, so all you should have to do is download and unzip the file, cd to BreezySLAM/python, and do
sudo python3 setup.py installFor a quick demo, you can then cd to BreezySLAM/examples and do
make pytestThis will generate and display a PGM file showing the map and robot trajctory for the Lidar scan and odometry data in the log file exp2.dat. If you have the Python Imaging Library installed, you can also try the log2png.py script to generate a a PNG file instead. If you have installed Matplotlib, you can see a “live” animation by doing
make movieYou can turn off odometry by setting the USE_ODOMETRY parameter at the top of the Makefile to 0 (zero). You can turn off the particle-filter (Monte Carlo position estimation) by commenting-out RANDOM_SEED parameter.
To see what other features are available, do
pydoc3 breezyslamBy using the component classes Map, Scan, and Position and the distanceScanToMap() method, you can develop new algorithms and particle filters of your own.
sudo make installThis will put the libbreezyslam shareable library in your /usr/local/lib directory. If you keep your shared libraries elsewhere, just change the LIBDIR variable at the top of the Makefile.
For a quick demo, you can then cd to BreezySLAM/examples and do
make cpptest
Again, you'll need to change the LIBDIR variable at the top of the Makefile in this directory as well, if you don't use /usr/local/lib.
To build and use the C++ library on Windows, I used MinGW. Whatever C++ compiler you use, you'll have to add the location of the .dll file to your PATH environment variable in the Advanced Systems Settings.